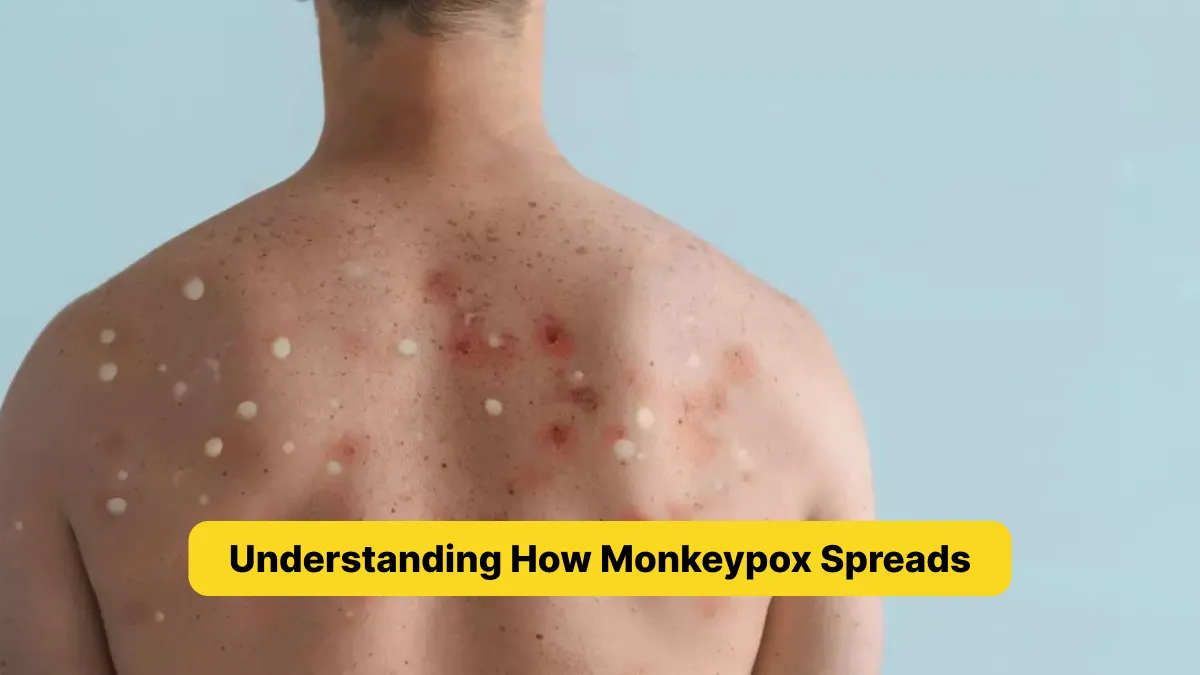
Monkeypox is a viral disease that has recently gained global attention. The virus is part of the same family as the one that causes smallpox, but monkeypox is generally less severe. However, it is essential to understand how monkeypox spreads to prevent its transmission. This article explains the various ways monkeypox can spread, including person-to-person transmission, animal-to-human transmission, and environmental factors.
Person-to-Person Transmission
One of the primary ways monkeypox spreads is through direct contact with an infected person. The virus can enter the body through broken skin, even if the break is not visible. It can also enter through the respiratory tract or mucous membranes, such as the eyes, nose, or mouth.
Direct Skin Contact
Monkeypox is most commonly spread through close contact with an infected person’s skin. If you touch the rash, sores, or scabs of someone with monkeypox, you can become infected. This type of direct contact is the most frequent mode of transmission. For example, in households where one person is infected, others are at risk if they come into contact with the infected person’s skin.
Respiratory Droplets
Another way monkeypox spreads is through respiratory droplets. When an infected person coughs or sneezes, tiny droplets are released into the air. These droplets can carry the virus and infect anyone who breathes them in. However, transmission through respiratory droplets usually requires prolonged face-to-face contact, making this method less common than direct skin contact. Despite this, it is still a significant route, especially in close living conditions or healthcare settings.
Contaminated Objects
The virus can also spread through contact with objects that have been contaminated by an infected person. This includes clothing, bedding, or towels that have come into contact with the rash or body fluids of someone with monkeypox. If another person touches these contaminated items and then touches their face or an open wound, they can become infected.
Animal-to-Human Transmission
Monkeypox is a zoonotic disease, meaning it can spread from animals to humans. The virus is naturally found in some animal species, including rodents and primates, in parts of Africa. When humans interact with these animals, especially in areas where monkeypox is more common, they are at risk of contracting the virus.
Bites and Scratches
One of the most direct ways for the virus to jump from animals to humans is through bites or scratches. If an infected animal bites or scratches a person, the virus can enter the body through the wound. This type of transmission is particularly concerning in areas where monkeypox is endemic, and people may come into regular contact with wild animals.
Handling Infected Animals
Handling animals that are infected with monkeypox can also lead to transmission. This is particularly true for people who work with or consume bushmeat, as these practices can bring them into close contact with infected animals. If a person handles or prepares meat from an infected animal, the virus can enter the body through breaks in the skin or through contact with mucous membranes.
Environmental Factors
Environmental factors can also play a role in the spread of monkeypox. The virus can survive on surfaces for a limited time, especially in cool and dry conditions. This means that people can potentially become infected by touching contaminated surfaces, although this method of transmission is less common.
Surface Contamination
As mentioned earlier, objects and surfaces that have come into contact with an infected person can harbor the virus. This includes anything from door handles to medical equipment. While surface transmission is less frequent, it is still possible, especially in healthcare settings where proper disinfection procedures are not followed.
Airborne Particles
In rare cases, the virus may spread through airborne particles, similar to how other respiratory viruses spread. This can happen when the virus becomes aerosolized, meaning it is carried through the air in tiny particles. However, this method of transmission is not common and typically requires specific environmental conditions.
Preventing the Spread of Monkeypox
Understanding how monkeypox spreads is crucial for preventing transmission. The best way to avoid getting monkeypox is to minimize direct contact with infected individuals or animals. If you are in an area where monkeypox is present, take extra precautions. Avoid close contact with sick people or animals, and practice good hygiene, such as washing your hands frequently.
Protective Measures
Wearing protective clothing, such as gloves and masks, can also reduce the risk of transmission, especially for healthcare workers or those caring for infected individuals. In areas where monkeypox is more common, it is important to be cautious around animals and to avoid handling wild animals.
Vaccination
Vaccination is another effective method to prevent the spread of monkeypox. The smallpox vaccine has been shown to provide protection against monkeypox. In some cases, vaccination after exposure can reduce the severity of the disease.
Conclusion
Monkeypox is a serious disease, but understanding how it spreads can help reduce the risk of transmission. Whether through direct contact, respiratory droplets, or contaminated objects, the virus can spread in various ways. Additionally, the virus can jump from animals to humans, particularly in areas where monkeypox is endemic. By taking proper precautions and understanding the risks, you can help prevent the spread of this disease.